FEMA and International Taxation
- Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act, 2010
- Accounts & Audit
- All FCRA services online
- Applicability
- Change of designated bank account, name, address, aim, objects or key members of the association
- Declaration of receipts of foreign contribution
- Foreign Contribution
- Inspection & Seizure
- Introduction
- Penalty
- Registration of the Association
- Restriction on Administrative Expenses
- Restrictions on acceptance of foreign hospitality
- Restrictions on Accepting FC
- Speculative Activity
- Total Ban on acceptance of Foreign Contribution & Hospitality
- Transfer of FC to other Registered or Unregistered Persons
- Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999
- Acquisition and transfer of Immovable property in India
- Acquisition and Transfer of Immovable Property outside India
- Bank Accounts in India
- Borrowings from Non-residents
- Branch/Liaison/Project Office in INDIA
- Branch/Liaison/Project Office outside India
- Capital & Current Account Transactions
- Compounding & Contravention under FEMA
- Cross Border Merger Regulations
- Introduction
- Investment in India
- Miscellaneous
- Overseas Direct Investments
- Residential Status under FEMA
- Trade Transactions – Import & Export
- International Taxation
Investment in India
Foreign Investment in India
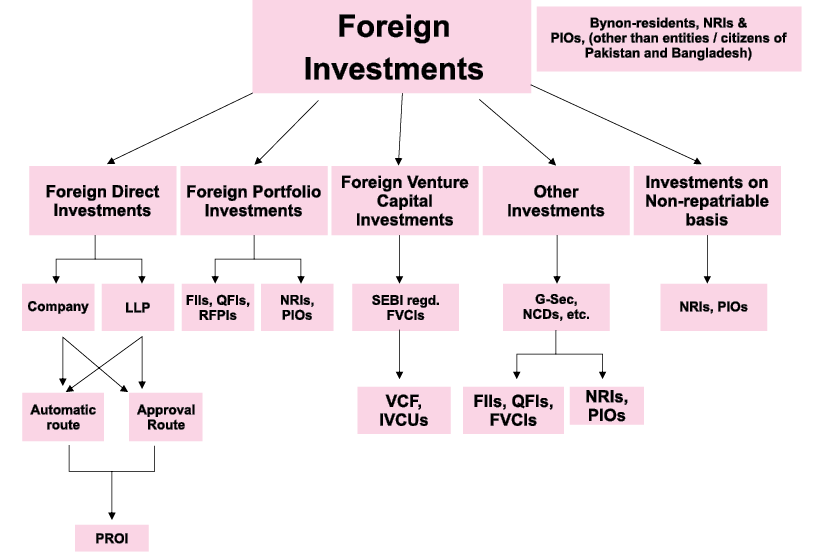
I. Foreign Direct Investment
The Industrial Policy, Foreign Exchange Management (Non-Debt Instrument) Rules (2019) and Mode of Payment and Reporting of Non-Debt Instruments Regulations, 2019 governs the Foreign Direct Investment in India. Both – Non Debt Instrument Rules and Industrial Policy (including consolidated FDI Policy) – should be read together to have a full picture. Sectoral limits for Foreign Direct Investments and Investments by NRIs are almost at par excepting the sector of Housing and Real Estate Development, and Domestic Airlines. Various avenues and policy for foreign investment are covered in brief. For FDI purposes an NRI means an individual resident outside India who is a citizen of India.
Investment is generally allowed in an Indian company, which is engaged in any business, except prohibited sectors. Branches, liaison offices and project offices can be opened for limited purposes. In SEZs, non-residents can invest as a branch/unit, Joint Venture or a Wholly Owned Subsidiary on automatic basis. Investment in a proprietorship, partnership or Association of Persons, is subject to RBI permission in certain cases.
Investment can be made by an incorporated entity, or individuals. Unincorporated entities cannot invest. However, citizens and incorporated entities of a country which shares land border with India (i.e. China, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Nepal, Myanmar and Afghanistan) or where the beneficial owner of an investment into India is situated in or is a citizen of any such country, are permitted to invest under the FDI scheme only after obtaining prior Government approval. Further, citizens and incorporated entities of Pakistan are prohibited to invest in defence, space, atomic energy and sectors/activities prohibited for foreign investment.
Also, any transfer of ownership of any existing or future FDI in an entity in India, directly or indirectly, resulting in the beneficial ownership by an entity/citizen as mentioned above, then such subsequent change will require prior Government approval.
|
Eligibility |
Person Resident Outside India |
|---|---|
|
Eligible Instruments |
Equity Instruments which is defined as Equity Shares, Convertible Debentures, Convertible Preference Shares, Partly paid Equity Shares and Share Warrants issued by an Indian Company subject to Company’s Act, 2013 & SEBI guidelines |
|
Lock in Period in case of optionality clause |
One year from the date of investment or as per prescribed FDI guidelines, whichever is higher |
|
Modes of Investment |
Issuance of fresh Shares or Transfer of Existing Shares |
When investment in India can be made in ANY sector without any approval from any authority, this is known as the “Automatic route”. For a small list of sectors or investment exceeding permissible sectoral caps, which are not under the “automatic route”, a specific approval should be taken from Government of India/Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) through the Foreign Investment Facilitation Portal (FIFP).
FDI is prohibited in the following activities/sectors:
- Lottery business including Government/private lottery, online lotteries, etc.
- Gambling and betting including casinos etc.
- Chit funds
- Nidhi company
- Trading in Transferable Development Rights (TDRs)
- Real Estate Business or Construction of Farm Houses (For FDI Regulations - “real estate business” shall not include development of townships, construction of residential /commercial premises, roads or bridges and Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) registered and regulated under the SEBI (REITs) Regulations 2014)
- Manufacturing of cigars, cheroots, cigarillos and cigarettes, of tobacco or of tobacco substitutes
- Activities/sectors not open to private sector investment e.g., Atomic Energy.
- Foreign technology collaboration in any form including licensing for franchise, trademark, brand name, management contract is also prohibited for Lottery Business and gambling and betting activities.
FDI is also permitted in LLPs
- Entry Route – Automatic route in LLP’s operating in sectors/ activities where 100% FDI is allowed through Automatic Route and there are no FDI linked performance conditions.
- Capital Contribution - An LLP can receive foreign capital contribution only by cash consideration, received by inward remittance, through normal banking channels or by debit to NRE/FCNR account of the person concerned, such account being maintained with an authorised dealer/ bank.
- Investment in LLPs by Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) and Foreign Venture Capital Investors (FVCIs) is not permitted.
- LLPs are not permitted to avail External Commercial Borrowings (ECBs).
FDI in LLP is subject to compliance of the LLP Act, 2008
Reporting Requirements
All reportings for various types of Foreign Investments in India are required to be done through the Single Master Form (SMF) through the Foreign Investment Reporting and Management System (FIRMS) portal. This includes the following -
- FC-GPR – which a company submits to RBI for reporting the issue of eligible instruments to the overseas investor.
- FC-TRS – which the non-resident has to submit at the time of transfer of shares/debentures between a resident and a non-resident.
- DI – which the downstream investment company has to submit at the time of indirect foreign investment or downstream investment.
- InVI – which the investment vehicle receiving investment has to submit at the time of issue of unites to overseas investors.
- LLP - I – which the LLP has to submit for reporting receipt of foreign direct investment by way of capital contribution and profit share.
- LLP - II – which the LLP has to submit for reporting disinvestment or transfer of capital contribution and profit share.
- ESOP – which the company has to submit for issue of ESOPs or Sweat Equity Shares or Shares against exercise of ESOP to employee outside India.
- CN – which the company has to submit for issue or transfer of convertible notes to overseas investors.
- DRR – which the company has to submit for issue or transfer of depository receipts to overseas investors.
The forms are required to be filed online. The certificates and other documents to be filed have to be scanned and uploaded along with the same. In cases where pricing guidelines apply, a Valuation report issued by a Chartered Accountant or a SEBI registered Merchant Banker is required to be submitted.
Further, every year before July 15, Annual return on Foreign Liabilities and Assets has to be filed directly with the Director, Balance of Payment Statistical Division, RBI detailing all investments by way of direct/portfolio/re-invested earnings/ others in the Indian company during the preceding financial year through the Foreign Liabilities and Assets Information Reporting (FLAIR) system.
Foreign Portfolio Investor (FPIs)
FPIs such as Pension Funds, Investment Trusts, Asset Management Companies, etc., who have obtained registration from SEBI, are permitted to invest on full repatriation basis under FDI Policy as well as under in the Indian Primary & Secondary Stock Markets (including OTCEI) including in unlisted, dated Government Securities, Treasury Bills, ‘to be listed’ debt securities, Units of Domestic Mutual Funds and commercial paper without any lock-in period.
Limits on investments are:
- The total holdings of all FPIs in any Company will be subject to its sectoral foreign investment cap. However, the company has an option to limit it to a lower threshold.
- A FPI, having 10% or more than 10% of total paid-up capital on a fully diluted basis or paid up value of each series of debentures or preference shares or share warrants, the total investment made by the FPI shall be re-classified as FDI subject to the conditions as specified by SEBI and RBI.
- A FPI may trade in all exchange trade derivative contracts approved by SEBI from time-to-time subject to the limits as prescribed in by SEBI.
An FPI may undertake short selling as well as lending and borrowing of securities as permitted by RBI and SEBI subject to certain conditions.
II. Foreign Venture Capital Investor (FVCI)
Foreign Venture Capital Investors (FVCIs) can invest in securities, issued by an Indian Company engaged in sectors which are permitted for the same and even those securities which are not listed on recognised stock exchange at the time of issue of such securities. They can also invest in securities issued by a Start-up enterprise irrespective of their sector/activity.
A registered FVCI may, through the SEBI, apply to the Reserve Bank for permission to invest in a VCF or in a scheme floated by such VCFs. The domestic VCF must however be registered with SEBI. The registered FVCI may purchase equity/ equity linked instruments/ debt/ debt instruments, debentures of a VCF through Initial Public Offer or Private Placement or in units of schemes/funds set up by a VCF.
The amount of consideration for investment in VCFs shall be paid out of inward remittance from abroad through normal banking channels or a Special Non-Resident Rupee (SNRR) account maintained in accordance with the FEM (Deposit) Regulations, 2016.
There is no limit on investments, but if the investment is in equity instruments then the sectoral caps, entry routes and attendant conditions shall apply. Form FC-GPR – Part ‘A’ has to be filed with RBI, through the company’s bankers, within 30 days of allotment of securities. Form FC-TRS will be applicable in case of transfer of shares between a resident and non-resident.
III. International Financial Institutions
Multilateral Development Banks, which are specifically permitted by the Government to float rupee bonds in India, are permitted to purchase Government dated securities.
IV. Investments by Non-Resident Employees of Indian Companies, etc.
An Indian Company can issue shares up to 5% of its paid-up capital to its employees or employees of its overseas joint venture or wholly owned subsidiary resident outside India, under a SEBI approved Employees Stock Options Scheme. These shares cannot however be issued to employees who are citizens of Pakistan/Bangladesh without Government Approval.
V. Investments by NRIs / PIOs
NRIs and Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) can invest in shares and convertible debentures of Indian companies.
Foreign investment policy for foreigners applies equally to NRI for repatriable investment. There are only two sectors – Real Estate Development and Domestic Airlines – where investment facilities are different for NRIs and foreigners.
|
Investment by NRIs |
Repatriation Basis |
Non-Repatriation Basis |
|---|---|---|
|
Permitted Instruments |
All instruments permitted under FDI for other non-residents, Government dated Securities (other than Bearer Securities), Treasury bills, Units of domestic Mutual Funds, bonds issued by PSUs in India, shares in Public sector enterprise disinvested by GOI |
All the instruments permitted under FDI for other non-residents, Government Securities (other than Bearer Securities), Treasury Bills, Units of Domestic Mutual Funds, Units of money market mutual funds |
|
Prohibited Instruments |
Investment in small saving schemes (including PPF) |
Investment in small saving schemes (including PPF) |
|
Deposit of sale proceeds |
No restrictions |
To be deposited in NRO Account |
RBI has granted general permission to NRI / PIO to acquire shares from other NRI / PIO. Purchase of shares by NRIs from existing resident shareholders is permitted under the automatic route if the specified conditions are satisfied.
NRIs from Nepal are also permitted to make direct investments on repatriation basis if they remit funds in foreign exchange.
Portfolio Investment in companies, other than those engaged in the print media sector, listed on Stock Exchanges is permitted up to 5% for each NRI subject to overall ceiling of 10% of the company’s capital. The company concerned can increase this limit of 10% to 24%.
NRI may invest in exchange traded derivative contracts approved by SEBI from time-to-time out of INR funds held in India on non- repatriation basis subject to the limits prescribed by SEBI.
NRIs are permitted to invest up to 100% in PSE Capital/PSU Bonds, Government Securities (other than Bearer Securities), units of UTI & instruments of domestic Mutual Funds (referred to in Section 10 (23D) of the Income-tax Act, 1961).
Consideration for purchase of the equity instruments should be received as inward remittance through banking channels or through funds held in NRE account, which is designated as NRE (PIS) Account used exclusively for investments on repatriation basis. NRIs are now permitted to credit the sale proceeds of FDI investment in their NRE/FCNR (B) accounts, provided the investment was received by way of remittance from abroad or by way debit to NRE/FCNR (B) account of the investor.
NRI / OCI can also invest on non-repatriation basis in all sectors except plantations, nidhis, chit funds and real estate trading. In such cases investments made on repatriation basis will also not apply. Investments made on non-repatriation basis is deemed to be domestic investment at par with investment made by residents.
NRIs can repatriate their investments which were originally made on non-repatriation basis subject to RBI approval if:
- The original investment was made in foreign exchange under the FDI Scheme, and
- The sector / activity in which the investment was made is proposed to be converted into repatriable equity and is under the automatic route for FDI.
If the above two conditions are not met, approval will have to be obtained from RBI for conversion of non-repatriable equity into repatriable equity.
VI. Conversion into equity
An Indian company can issue, subject to certain terms and conditions, equity shares / preference shares under the Approval Route:
- By way of conversion of ECB (other than import dues deemed as ECB or Trade Credit), lump sum technical knowhow fees, royalty or any other funds payable by the investee company, remittance of which does not require prior permission of the Government of India or RBI.
- By way of conversion of monies payable against import of capital goods/machineries/equipment (other than second- hand machineries).
- Against receipt of money from overseas investor towards pre-operative/pre-incorporation expenses (including payments of rent, etc.).
VII. Investment Facilities in brief
|
Avenues of Investment |
Instruments |
Category of Investors |
|---|---|---|
|
Public/Private Limited Companies |
‘Equity instruments’, which means equity shares, compulsorily convertible preference shares, compulsorily convertible debentures and share warrants issued by an Indian Company |
Non-Resident Indians/Person resident outside India/ Non-Resident Incorporated Entities/ Foreign Institutional Investors |
|
Public Limited Companies |
NCDs |
NRIs |
|
Trading Companies |
‘Equity instruments’, which means equity shares, compulsorily convertible preference shares, compulsorily convertible debentures and share warrants issued by an Indian Company |
Person resident outside India |
|
MSME Units |
‘Equity instruments’, which means equity shares, compulsorily convertible preference shares, compulsorily convertible debentures and share warrants issued by an Indian Company |
Person resident outside India |
|
EOU or Unit in Free Trade Zone or in Export Processing Zone |
‘Equity instruments’, which means equity shares, compulsorily convertible preference shares, compulsorily convertible debentures and share warrants issued by an Indian Company |
Person resident outside India |
|
Public/Private Ltd. Companies |
Equity instruments including Right Share other than share warrants |
Existing shareholders / Renouncees |
|
Under Scheme of amalgamation/ merger |
‘Equity instruments’, which means equity shares, compulsorily convertible preference shares, compulsorily convertible debentures and share warrants issued by an Indian Company |
Existing shareholders |
|
Employees Stock Option |
‘Equity instruments’, which means equity shares, compulsorily convertible preference shares, compulsorily convertible debentures and share warrants issued by an Indian Company |
Employees resident outside India |
|
ADR/GDR |
Receipts |
Non-residents |
|
Portfolio Investment Scheme |
‘Equity instruments’, which means equity shares, compulsorily convertible preference shares, compulsorily convertible debentures and share warrants issued by an Indian Company |
RFPIs (Registered Foreign Portfolio Investor) & NRIs |
|
Investment in Derivatives |
Exchange Traded Derivatives |
RFPIs (on repatriation basis) & NRIs (on repatriation basis) |
|
Govt. Securities |
Govt. dated Securities/Treasury Bills, Units of Domestic Mutual Funds, Bonds issued by PSUs and shares of Public Sector Enterprises being divested |
NRIs & RFPIs |
|
Indian VCU or VCF or in a Scheme floated by VCF |
SEBI Registered VCF/VC Units |
SEBI Registered Foreign Venture Capital Investor |