Allied Laws
- Arbitration & Conciliation Act, 1996
- Benami Transactions (Prohibition) Amendment Act, 2016
- Capital Market/SEBI Regulations
- Chartered Accountants Act and Regulations
- Checklist for Mergers, Demergers and Slump Sale
- Competition Act, 2002
- Consumer Protection Act, 1986
- Employees Stock Options and Ownership Plans (ESOPs)
- Fees – Recommended by ICAI
- Indian Registration Act
- Information Technology Act
- Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 (IBC)
- Labour Laws
- Leave and Licences
- Limited Liability Partnership
- Maharashtra Public Trusts Act, 1950 as amended by Maharashtra Public Trusts (Second Amendment) Act, 2017 Charity Commissioner (C.C.)
- Maharashtra Stamp Act, 1958
- NBFC Directions, 1998
- Partnership Firms – Procedures (Maharashtra)
- Period of Preservation of Accounts/Records under Different Laws
- Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002
- Real Estate (Regulation & Development) Act, 2016
- Right to Information Act, 2005
- SEBI (Alternative Investment Funds) Regulations, 2012
- SEBI (Investment Advisers) Regulations, 2013
- SEBI Listing Regulations
- SEBI Takeover Regulations, 2011
- Succession and Wills
- The Banning of Unregulated Deposit Schemes Act, 2019
- The Maharashtra E-Payment of Stamp Duty and Refund Rules, 2013
- The Maharashtra e-Registration and e-Filing Rules, 2013
- The Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Development Act, 2006
- Transfer and Transmission of Flats
- Valuation
Chartered Accountants Act and Regulations
1. Provisions
- Statute
- The Chartered Accountants Act, 1949.
- As amended by The Chartered Accountants (Amendment) Act, and 2006 (updated as on 1st July, 2013).
- The Chartered Accountants Regulations, 1988.
- Membership Eligibility (Ss. 4 & 8 and Regn. 4)
- The applicant should have
- Completed prescribed period of practical training.
- Passed the CA Final Examination.
- Attained twenty-one years of age.
- Completed the course on General Management & Communication Skills (GMCS)
- Applied in Form 2 on ICAI Self Service Portal, with the prescribed membership and entrance fees.
- The applicant should have
- Eligibility to join the CA Course & Examinations (Regn. 45)
- Eligibility for Common Proficiency Test (CPT) (Regn. 25C & 25D) – May enroll for the course if passed Class 10 examination. May appear for CPT after appearing for Senior Secondary Examination (10 + 2) Examination or while positive result of the same is awaited. CPT Examination will be generally conducted two times a year (student who has got himself registered 60 days prior to the first day of the month in which CPT examination is to be held i.e. on or before 1st April and 1st October, can appear in the CPT examination to be held in June and December respectively). It is a test of four subjects viz., Accounting, Mercantile laws, General Economics and
Quantitative Aptitude (tests the basic knowledge in these subject areas). (Refer to New Course Guidelines) - Eligibility for Registration as Articled /Audit Assistant: Such a person has passed CPT / New Foundation and Group I of IPCC / New Intermediate. CA student has to complete 100 hrs. or I.T.T. course and 35 hrs. of orientation course before joining articleship.
- Eligibility for Common Proficiency Test (CPT) (Regn. 25C & 25D) – May enroll for the course if passed Class 10 examination. May appear for CPT after appearing for Senior Secondary Examination (10 + 2) Examination or while positive result of the same is awaited. CPT Examination will be generally conducted two times a year (student who has got himself registered 60 days prior to the first day of the month in which CPT examination is to be held i.e. on or before 1st April and 1st October, can appear in the CPT examination to be held in June and December respectively). It is a test of four subjects viz., Accounting, Mercantile laws, General Economics and
- Integrated Professional Competency Course (IPCC) / New Intermediate
- Requirements for IPCC / Intermediate Registration:
Pass in 12th standard and CPT Exam (or Entrance/Foundation/PE-I)
- Requirements for appearance in IPCC /Intermediate Exam Completion of 9 months study course
- Requirements for IPCC / Intermediate Registration:
- Direct Entry to Chartered Accountancy Course
Exempted Categories: The following categories of students shall be exempted from passing the Common Proficiency Test (CPT):
- Graduate or Post Graduate in Commerce having secured in aggregate a minimum of 55% of the total marks or its equivalent grade in the examination conducted by any recognised University (including Open University) by studying any three papers of 100 marks each out of Accounting, Auditing, Mercantile Laws, Corporate Laws, Economics, Management (including Financial Management), Taxation (including Direct Tax Laws and Indirect Tax Laws), Costing, Business Administration or Management Accounting; or
- Graduates or Post Graduates other than those falling under Commerce stream mentioned above having secured in aggregate a minimum of 60% of the total marks or its equivalent grade in the examination conducted by any recognised University (including Open University) OR has passed the intermediate level exam of ICWA or ICSI.
For more details, please visit website www.icai.org (BOS/Announcement/227/12(1) dated 16th August, 2012.
- Final Examinations (Regn. 29)
Examination held in May and November every year. Conditions for eligibility as given below:
- Should have passed Intermediate/PE-II Examination/ Professional Competence Examination (PCE)/IPCC / Intermediate
- Should have completed or is serving the last twelve months of Articleship as on the first day of the month in which the examination is held. (applicable in case of three years articleship; i.e., for the students who commence articles after PE II)
- Should have completed or is serving the last 6 months of articleship as on the first day of the month in which examination is held (applicable to students who commence articles after CPT, for a period of three and half years or IPCC / Intermediate for a period of 3 years)
- Members Entitlement to train articled assistant (Regn. 43)
Eligibility requirement for member giving practical training
- Member should be in full time practice.
- No. of trainees (articled assistants) given below:
|
No. of years in Practice |
No. |
|---|---|
|
0-3 years |
1 |
|
3-5 years |
3 |
|
5-10 years |
7 |
|
10 yrs. and above |
10 |
In addition to the above full-time salaried employees who have continued as employee with the same employer for 3 years as on the date of registering as articled assistant shall also be entitled to give practical training as under –
|
Total number of members – irrespective of whether associate or fellow, who are full time salaried employees |
Entitlement for articled trainees |
|
Up to 100 |
1 per employee |
|
Between 101 and 500 |
100 + 50% of the number of such employees above 100 (i.e., a maximum of 300) |
|
From 501 or more |
300 + 20% of the number of such employees above 500 |
In case of discontinuance of practice, or resignation of partner such member shall not be entitled to train article assistant/s for the balance of their training period. Such articled assistant/s will continue to be trained in the same firm even though the other partners are already training up to their maximum entitlement.
- Practical Training Record (Regn. 64)
A monthly record of practical training of the Articled/Audit Assistant is required to be maintained w.e.f. 1-4-1995 in respect of all articled trainees commencing articles thereafter.
- A monthly training record specifying the areas in which the articled assistant has obtained work experience with corresponding No. of days is to be maintained by the member in charge of training (MIT) or Principal.
- A report of the practical training on the basis of such monthly record is to be enclosed with Forms 108/109 [Regulations 64(1) & 64(2)], in all cases of completion/termination.
(Refer Training Guide issued by the Institute)
- Stipend for Articled Assistant (Regn. 48)
Minimum monthly stipend as shown below (w.e.f. 23rd January, 2015)
|
Population of normal place of service |
1st year |
2nd year |
3rd year |
|---|---|---|---|
|
20 lakh or above |
2,000 |
2,500 |
3,000 |
|
4 lakh or more but below 20 lakh |
1,500 |
2,000 |
2,500 |
|
Below 4 lakh |
1,000 |
1,500 |
2,000 |
Payment to be made by account payee cheque or credit to bank account of articled assistant. Stamped receipt to be obtained by principal.
Population figures on the basis of last published census figures.
- Leave (Regn.59)
Entitlement of leave** = Period worked (excluding leave) /6
** Subject to a maximum entitlement of 180 days leave for three and half years articleship and 156 days for three years articleship. Stipend is payable only for such period and not for period of excess leave taken.
- Period of training (Regn. 50, 71)
Article assistant 3 years & 6 months for PCC students, 3 years for PE-II qualified students. 3 years for IPCC – GI qualified students
Audit assistant 56 months for PCC students and 4 years for PE-II/ IPCC qualified students
- Transfer/Termination of Articleship [Regulation 56(1)]
In partial modification of the announcement dated 30th June, 2009 regarding transfer/termination of articles the Council in its recent meeting has decided that the transfer/termination of articleship in terms of Regulation 56(1) of the Chartered Accountants Regulations, 1988 shall be permissible on the grounds as stated below: –
- Transfer/termination of articles is permitted without any restriction during the first year of articles.
- During rest of the articleship period on satisfying anyone or more of the conditions as stated below: –
- Medical grounds requiring discontinuance of articles for a minimum period of three months (on production of a Medical Certificate issued by a Government Hospital).
- Transfer of parent(s) to another city.
- Misconduct involving moral turpitude.
- Other justifiable circumstances/reasons: —
- Grounds already permissible in the Chartered Accountants Regulations, 1988 (on submission of requisite proof of the Act warranting transfer/termination of articleship): —
- Industrial Training (Regulation 51)
- Secondment of articles (Regulation 54)
- Conversion from PCC to IPCC (for termination of articles only.
Re-registration of articles to be allowed only after passing Group-I of IPCC) - Death of Principal [Regulation 57(1)(c)]
- Ceasing of practice by the Principal [Regulation 57(1)(a)]
- Removal of name of the Principal from the Register of Member due to any reason [Regulation 57(l)(b)]
- Marriage (only if there is relocation to another city involving distance of 50 kms).
- Irregular payment or non-payment of stipend with reference to Regulation 67.
- Articled assistant desires to serve balance period of training outside India.
- Shifting by the Principal to another city involving distance more than 50 kms.
- Grounds already permissible in the Chartered Accountants Regulations, 1988 (on submission of requisite proof of the Act warranting transfer/termination of articleship): —
The articled assistants are required to get the consent of the Institute before getting Form 109 filed on ICAI Self Service Portal with consent OTP by the Principal in their own interest.
The request, on anyone or more of the aforesaid grounds of an articled assistant on a plain paper along with the recommendation/ consent of the Principal for transfer/termination of articleship accompanied by evidence/proof (self-attested by the articled assistant) to the satisfaction of the Institute be made. Request for transfer not accompanied by consent of Principal shall not be accepted. Not applicable in case of Transfer for Industrial Training
In case of dispute between Principal and articled assistant, the matter be settled amicably among the articled assistant and the Principal concerned and the Institute shall not interfere in such cases.
- Training in Industry (Regn. 51, 72)
- Eligibility: Articled or audit assistant passing Intermediate/PE-II/PCC/IPCC Examination.
- Period: Minimum period may range between 9 and 12 months during last year of practical training.
- Only with recognised financial/commercial/industrial undertaking with minimum fixed assets of ₹1 crore or minimum total turnover of ₹10 crore or a minimum paid-up share capital of ₹ 50 lakh or in any other institution or organisation approved by the Council.
- Training under a member of the Institute who has been a member for continuous period of at least three years. (Associates-1 trainee. Fellows- 2 trainees)
- Intimation of intention to Principal under whom serving earlier, at least three months in advance.
- Agreement in triplicate in Form 104 to be executed.
- Office hours (Regn. 60)
- An articled assistant shall work 35 hours per week.
- The articled assistant should undergo practical training in accordance with the guidelines of the Institute between 9.30 a.m. and 5.30 p.m.
- The articled assistant shall not be permitted to attend colleges/other institutions for graduation or any other course between 9.30 a.m. and 5.30 p.m.
- Every articled/audit assistant shall submit, once in a year, a specific declaration duly countersigned by the Principal to the effect that he is regularly attending training and his college hours do not clash with his articles timings and that no coaching is undertaken by him between 9.30 a.m. and 5.30 p.m. on any working day.
- Other courses of study during training (Regn. 65)
- Cannot be undertaken without prior permission of the Council of the Institute.
- Permission is normally granted on a specific prior application in Form 112 for permission in respect of all courses other than those specified in a negative list that may be specified by the Council from time to time.
- In case of attending of regular classes, the same should be outside normal office hours.
- Only one course permitted at a time during training period.
- In the event of breach of guidelines and not taking permission as required, the articles already undergone shall be derecognised for such period as the Institute may decide. In case an articled assistant is found not undergoing articles in the manner prescribed, he shall be debarred from appearing in the exam up to 3 consecutive exams besides cancellation of such period of articles. The concerned member who allowed him to be such an articled assistant be subject to punitive action besides withdrawing either partly or fully his eligibility to train articled assistant. In Peer Review, the reviewer be required to verify whether training is imparted to the articled assistants in the manner prescribed.
Other occupation during training (Regn. 65)
- Cannot engage without permission of Council.
- Permission normally granted for being sleeping partner in a firm, directorship in a family company and lectureship in college (not exceeding 9 hours per week) in subjects
useful for CA course, subject to fulfilment of certain conditions.
Implementation of New GMCS Programme
The Council has decided that the General Management and Communication Skills (GMCS) Programme, presently being organised for 15 days for the CA students should be organised twice during the period of articled training as under:
- GMCS-I (15 days) – during 1st year of articled training
- GMCS-II (15 days) – after completion of 18 months of training but before completion of articled training
In view of the same GMCS-I & II Programmes will be implemented in respect of those students, who will be registered for articled training on or after 1st May, 2012. Students, who are undergoing articled training or have been registered for articled training prior to 1st May, 2012 shall be governed by the existing GMCS Scheme. The fee for each programme of GMCS I & II shall be ₹ 9,000/- only.
ICAI New Scheme of Education & Training 2018
Foundation Course will be the entry level Course for Chartered Accountancy Course. Students after appearing in class 12th examination conducted by an examining body constituted by law in India or an examination recognized by the Central Government as equivalent thereto, can register for this Foundation Course and appear after qualifying the said senior secondary (10+2) examination. Students after registration to the course are required to complete a minimum of 4 months study period from the date of registration in order to be eligible to appear in the Foundation Examination, i.e., students registered on or before 30th June/ 31st December will be eligible to appear in November/ May examination, as the case may be. Students who are Graduates/ Post Graduates with prescribed percentage marks or its equivalent grade in the examination conducted by any recognized University (including Open University) or Intermediate level examination passed students of The Institute of Cost Accountants of India or The Institute of Company Secretaries of India are exempted from passing Foundation Course. Such students on fulfilling the requirements can register directly to Intermediate Course. Foundation Course comprises of four papers, out of which two are subjective and two are objective type. Negative marking for choosing wrong options is there in objective papers.
ICAI will give some fixed number of attempts to complete CA CPT in old syllabus for old registration students.
The nomenclature for CA IPCC has been changed to CA Intermediate as per the new syllabus. There are 8 papers in CA Intermediate new scheme from 2016. ICAI introduced Financial Management & Economics for Finance subject in new syllabus.
There are 8 papers in CA Final new syllabus from 2016 as compared to 7 subjects in the old syllabus. ICAI introduced Elective Paper (100 Marks) in new syllabus. There are 6 options one has to choose from the list of Elective Papers – Risk Management; International Taxation; Economic Laws; Financial Services & Capital Markets; Global Financial Reporting Standards; Multidisciplinary Case Study
Further ICAI also introduced changes in Paper 7: Part I is Direct Tax Laws for 70 Marks & Part II is International Taxation for 30 Marks.
It is hereby clarified that the last exam under the Old Scheme for different levels will be held as follows:
Common Proficiency Test June, 2019
Intermediate (IPC)-Old Scheme May, 2019
Final (Old) Scheme November, 2020
(Refer ICAI ANNOUNCEMENT dated 18th January, 2018 of Transition Scheme for students of Common Proficiency Course, Intermediate (IPC) Course and Final (old) Course along with the Conversion Fees for Switching Over to Revised Scheme)
Miscellaneous
- Secondment
- The articled assistant can be seconded to another member eligible to train articled assistant/s by mutual consent. Student has to submit form for secondment to his Principal who after completing the same has to submit the same to Regional Office of ICAI.
- The Principal can, with the prior consent of the articled assistant/s, second the articled assistant/s to another eligible member as per above procedure.
The member to whom the articled assistant/s is seconded to should be eligible to train articled assistant/s.
Maximum articled assistant/s a member can train in case of secondment shall be 2.
Aggregate period of secondment shall not exceed 1 year, minimum duration under one member should be four months.
In case secondment done to a member in an industry the period shall not exceed 1 year.
Principal to
- Pay the stipend during secondment
- Keep record of training undergone in secondment.
No need to execute a separate deed in case of secondment.
- Commonly Used Forms – to be applied on The ICAI Self Service Portal
|
Form No. |
Description |
|---|---|
|
2 |
Application for Associate Membership |
|
3 |
Application for Fellow Membership |
|
6 |
Certificate of Practice |
|
9 |
Application for Restoration of Membership" |
|
18 |
Particulars of offices and firms |
|
101 |
Restoration of Certificate of Practice |
|
102 |
Agreement for Articled Assistantship |
|
104 |
Agreement for Industrial Training |
|
105 |
Completion/Termination of Industrial Training |
|
107 |
Supplementary Deed of Articles (on account of excess leave) |
|
108 to 113 & 117 |
Completion of Articled Assistantship, Terminations; Other engagements; Registration of Audit assistant; Approval of Firm Name |
Membership Fees
|
Particular |
Fees for all Members not holding |
Fees for Members of the age 60 years or above (as on 01.04.2019) but not holding Certificate of Practice |
|---|---|---|
|
Associate Membership Fee |
₹ 1,500 + 18% GST = 1,770 |
₹ 1,100/- + 18% GST = 1,298 |
|
Fellow Membership Fee |
₹ 3,000/- + 18% GST = 3,540 |
₹ 2,300/- + 18% GST = 2,714 |
Fees for all Members holding Certificate of Practice
|
Particular |
Associate Membership Fee |
Fellow Membership Fee |
|---|---|---|
|
Membership Fees |
1,500 |
3,000 |
|
Certificate of Practice fee |
3,000 |
4,000 |
|
GST @ 18% |
810 |
1,260 |
|
Total |
5,310 |
8,260 |
The aforesaid revised rates of fees shall come into force with effect from 9th April, 2019.
Recommended scale of fees for work done by Chartered Accountants
(Refer to guidelines of ICAI Committee for Capacity Building of Members in Practice – Visit “www.icai.org.in”)
3. Students Fees Payable
All fees are to be paid online through the ICAI Self service Portal.
- FOUNDATION COURSE FEE
|
S. No. |
Details of Fee |
₹ |
For Foreign Student US$ |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Cost of Prospectus |
200 |
20 |
|
2 |
Foundation Registration Fee |
9,000 |
700 |
|
3 |
Subscription for Students’ Journal (For one Year) (Optional) |
200 |
20 |
|
4 |
Subscription for Members’ Journal (For one Year) (Optional) |
400 |
40 |
|
Total |
9,800 |
780 |
- INTERMEDIATE COURSE FEE
|
Registration Options/Various charges |
Both Groups |
Both Groups |
Group I / II |
Group I / II |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
₹ |
US$ |
₹ |
US$ |
|
|
Registration fee |
15,000 |
11,000 |
||
|
Students’ Activities Fee |
2,000 |
2,000* |
||
|
Registration fee as articled assistant |
1,000 |
|||
|
Total Fees |
18,000 |
1,000 |
13,000 |
600 |
*to be paid once
Cost of Prospectus ₹ 200/- (US$ 20) to be paid by Direct Entry students in addition to above fees.
-
FINAL COURSE FEE
|
Details |
₹ |
For foreign students US$ |
|---|---|---|
|
Final Registration Fee* |
22,000 |
1,100 |
*Without Article
4. Code of Ethics Old – Some Provisions applicable till 30 June 2020
|
Sr. No. |
A practicing CA CANNOT |
A practicing CA CAN |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Solicit work |
Give his audit report to the client on his letterhead |
|
2 |
Give a client’s balance sheet on his letterhead. |
Use a prescribed logo on visiting cards, letterheads, etc. |
|
3 |
Describe on his letterhead or visiting cards association with other Indian/Foreign firms. |
Describe himself as a CA. in greeting cards and invitation cards. Can use the prefix CA. before his name. |
|
4 |
Use a firm name not approved by the Institute |
Advertise in the official Yellow pages brought out by the telephone authorities. |
|
5 |
Have his name displayed in Yellow pages in bold. |
Display his firm’s name board in a manner that it does not smack of advertisement. |
|
6 |
Advertise as per the notified guidelines. |
Website
The Institute has permitted each member to
- Establish their own websites
- Ensure that their Websites are run on a ‘pull’ model and not a ‘push’ model of the technology
- Ensure that any person who wishes to locate the member would only have access to the information
- Ensure the information should be provided only on the basis of specific ‘pull’ request.
Tenders
|
Sr. No. |
The Practicing CA CANNOT Respond to |
CAN Respond to Advertisement / Circular/Tenders or enquiries |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Advertisements inviting applications for appointment of auditors |
In other areas when competing with non CAs. |
|
2 |
Tenders or circulars or enquiry (made to more than one member) inviting quotations restricted to CA |
If the same has been sought by World Bank/IMF/ADB/Other similar International Body/Govt. Co. or Agency/Autonomous Body sponsored or regulated by the Govt./Nationalized Institution. |
|
3 |
In case of any other services, including audit services to be provided out of country |
|
|
4 |
A CA cannot pay earnest money/security deposit in areas which are exclusive to CA as per law |
A CA can pay
|
A practicing CA
- CAN be a director simplicitor in a company without prior permission of Council. [The expression “Director Simplicitor” means an ordinary / simple Director. A member in practice is permitted generally to be a Director Simplicitor in any Company including a board-managed Company and as such he is not required to obtain any specific permission of the Council in this behalf unless he or any of his partners is interested in such Company as an auditor, irrespective of whether he and/or his relatives hold substantial interest in that Company]
- CAN be a promoter or promoter director in a company without prior permission of Council.
- CAN be a Managing Director or Whole-time Director of a company with prior permission of Council. This permission is granted if such CA. and/or relative do not have substantial interest (i.e., more than 20%) in the company. However, w.e.f. 1-4-2005 the member is not permissible to do attest function.
|
Sr. No |
A practicing CA CANNOT |
A practicing |
|---|---|---|
|
1. |
Accept contingency or percentage based fees, except in the following cases:
|
CAN share fees with other practicing CA. but not with others. |
RULES OF NETWORK AND MERGER–DEMERGER
Refer to ICAI-Revised Guidelines of Networking-updated on 12th October, 2015.
Practical framework of Network
- Network is coming together of two or more firms to facilitate the better professional functioning of the affiliate member firms.
- The Network is formed by two or more Firms registered with ICAI.
- The approval of name is carried out by filing of Form ‘A’
- The Network is named by having the prefix “Affiliates/Members of ……” before the name of the network.
- The Network is registered by making an Application in Form “B”. The Application has to be signed by the Authorised Partners of all the firms constituting the Network.
- Only 1 Network is permissible per Firm amongst Indian firms.
- The Network with a Foreign Firm is to be registered by Filing of Form “D” with ICAI by the Indian Firm.
- Only 1 Network is permissible with a foreign firm.
- The withdrawal from the Network by any Firm can be done by Filing Form “C”.
Practical Framework of Mergers
- The Rules of Merger & Demerger are as notified by ICAI.
- The Merger takes place by Registration of a Merger Agreement in Form “E” to be submitted to ICAI.
- The Merger Agreement has to be filled within 30 days of the reconstituted Partnership Deed.
- Demerger can take place only if 75% or more of the Partners agree to Demerge.
- The Demerger takes place by submission of Form “F”. Demerger cannot take place after 5 years of Merger.
5. Audit
Appointment of Auditors – Section 139 of Companies Act, 2013
- Instead of reappointment at each AGM, auditor to be appointed for a block of five years.
- Reappointment needs to be ratified at each AGM.
- Appointment shall be made taking into recommendations of the Audit Committee/Board
- At each AGM, CA members will have option to:
- Rotate Audit partner/team
- Appoint joint auditor
- Maximum of 20 companies (including private limited companies) can be audited by an individual Auditor
- Auditors need to provide a written consent and also indicate whether they satisfy the criteria provided in Section 141 of Companies Act, 2013
- Firm includes an LLP incorporated under the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008
Rotation of Auditors – Section 139 of Companies Act, 2013
- Mandatory auditor rotation
Companies covered by rotation (Listed companies, unlisted public companies with paid-up share capital > ₹ 10 crore, private limited companies with paid-up share capital > ₹ 20 crore, all companies having public borrowings from banks/financial Institutions or public deposit > ₹ 50 crore)
- While a partnership firm would be eligible for two consecutive five year terms an individual auditor would be eligible for one such term.
- Term prior to commencement of Companies Act, 2013 will be retrospectively reckoned for computing 5-10 year validity.
- After completion of audit engagement term, the Auditor will be subject to a continuous five year cool off period.
- Incoming auditor cannot be an associate or from same network as the outgoing auditor.
- If a partner who is in charge of an audit firm and also certifies the financial statements of a company, retires from the said firm and joins another firm of chartered accountants, such other firm shall also be ineligible to be appointed for a period of five years.
- Where a company has appointed two or more persons as joint auditors the rotation shall be done in such a manner that all of the joint auditors do not complete their term in the same year.
Disqualification and Independence criteria – Section 141 of Companies Act, 2013
If:
- Officer/employee of company (or partner of/in employment of such person)
- Auditor in more than 20 companies
- Convicted by Court
- Body Corporate, other than LLP
- Holding security of/interest in or indebted to company/its subsidiary/associate/holding company/subsidiary of its holding company exceeding ₹1 lakh/ ₹ 5 lakh.
- Person whose relative is Director/KMP of company
- Full time employment elsewhere
Non-audit services – Section 144 of Companies Act, 2013
The following are the prohibited services by auditor and related entities, the transition period is 1 year:
- Management services
- Outsourced financial services
- Design and implementation of financial information system
- Investment advisory
- Actuarial services
- Investment banking
- Internal Audit
- Accounting & Book-keeping
- Any other prescribed service
Prohibition extends to holding and subsidiary companies.
All non-audit services to be approved by Audit Committee or Board of Directors
Duties and Liabilities of auditors – Sections 143 and 147 of Companies Act, 2013
|
Sr. No. |
Duties of Auditor u/s. 143 of the New Companies Act, 2013 |
Liabilities of Auditor u/s. 147 of the New Companies Act, 2013 |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Auditor to report on specified matters, in the audit report |
Contravention of provisions punishable with fine not less than ₹ 25,000 up to ₹ 500,000 |
|
2 |
Responsibility to report offence involving fraud to the Central Government |
In case of wilful or contravention done knowingly or with wilful intent to deceive, imprisonment up to one year and fine not less than ₹ 100,000 but which may extend up to ₹ 2,500,000 |
|
3 |
National Financial Reporting Authority can specify additional matters for reporting |
If convicted also liable to refund remuneration and liable to pay damages (to company, statutory bodies or authorities) arising out of the incorrect reporting |
Fraud reporting requirements – Section 143 and Rule 13 of Companies (Audit and Auditors) Rules
- Auditor to report within 2 days of knowledge of fraud to Board/Audit Committee
- Reporting of frauds by auditor involving amount more than ₹ 1 crore
- Audit Committee/Board must give response to Auditor within 45 days
- Within 15 days of receiving response, Auditor must report to Central Government the response along with his/her comments.(report even if no response is received)
- Reporting of frauds by auditor involving amount less than ₹ 1 crore
- Auditor must report to the Board/Audit Committee describing Approximate amount involved; and Parties involved
- Board Report to disclose: nature of fraud, approximate amount, parties involved, if remedial action not taken and remedial action taken.
- Fraud reporting provisions apply also to secretarial, cost auditors, branch auditor and internal auditor
- In case of non-compliance with the reporting obligation on frauds punishable with fine not less than ₹ 1 lakh but which may extend up to ₹ 25 lakhs.
Tax Audit under Income-tax Act
- Firm of CAs not to accept more than 60 tax audits per partner.
- Member not to accept more than 60 tax audits.
- Record of Tax Audit Assignments to be maintained. (Refer ICAI Journal May, 2003 page 1127 for the format)
- Tax Auditor cannot act as an Internal Auditor.
6. Other activities
|
Sr. No. |
A practicing CA CANNOT |
A practicing CA CAN |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Carry on any other business except with prior permission of the Council. |
Be involved in business through HUF so long as he is not Karta of HUF. |
|
2 |
Act as portfolio manager for his client. |
Carry on the profession of practicing Chartered Secretary, Cost Accountancy or as an advocate with prior permission of the Council and provided the other professional body permits the same. |
|
3 |
Express his opinion on the financial statements of a concern in which his relatives as defined under the Companies Act or such relatives along with himself are substantially interested. |
Be the author of any books or articles and act as editor of professional journals. |
|
4 |
— |
Hold office in an honourary capacity in a charitable, educational or other non-commercial organisation. |
Disclosure
|
Sr. No. |
A practicing CA CANNOT |
A practicing CA SHOULD |
|---|---|---|
|
1. |
Disclose confidential information relating to client to a third party without client’s permission or unless he is required to do so under law. |
— |
6A. Frequently Asked Questions on Code of Ethics -Existing
|
Question |
Answer |
Council Decision and Date / Condition |
|---|---|---|
|
Clarification on a member in practice being a Karta of a HUF making investment. |
A member in practice engaged as Karta of a Hindu undivided Family (HUF) doing family business will be within the limits prescribed by Council if he makes investments from the funds pertaining to HUF only, provided he is not actively engaged in the management of the said business |
S.N. 4 of “Permission to be granted specifically” of Appendix 9 to the Chartered Accountants Regulations, 1988 |
|
Clarification on prohibition of simultaneously undertaking Concurrent Audit and Quarterly Review of the same Bank |
Since queries are being received from members at large on the issue, it is accordingly hereby clarified that concurrent audit and the assignment of quarterly review of the same Bank cannot be undertaken simultaneously as the concurrent audit being a kind of internal audit and the quarterly review being a kind of statutory audit undertaken simultaneously are prohibited |
under the provisions of ‘Guidance Note on Independence of Auditors |
|
Whether a member can accept appointment as Statutory Auditor of certain branch(es) of a Bank, while he is the Revenue Auditor of different branch(es) of the same Bank |
No, a member is not permitted to accept the appointment as Statutory Auditor of certain branch(es) of a Bank while he is the Revenue Auditor of different branch(es) of the same Bank |
FAQ 22-04-2020 |
|
Whether the Internal Auditor of an entity/Bank can undertake 2 Consultancy work of the same Bank? |
There is no restriction for the consultancy work if it is undertaken by a member along with the assignment of Internal Audit |
FAQ 22-04-2020 |
|
Whether the Statutory Auditor of a Bank can accept Stock audit of the same branch or different branch of the same Bank |
The Stock Audit and Statutory Audit are not permissible to be done simultaneously since Stock Audit is kind of management function, which cannot be done simultaneously with the Statutory Audit (whether pertaining to the same branch of different branch) |
FAQ 22-04-2020 |
|
Whether the Concurrent Auditor of a Bank can accept Tax audit of the same Bank? |
No, the Concurrent Auditor of a Bank cannot accept the Tax audit assignment of the same Bank, as it would affect independence in terms of the provisions of Code of Ethics that Statutory Audit and Internal Audit cannot be done together, as also in terms of the provisions of Section 288 of the Income Tax Act, 1961 which prohibits undertaking Concurrent Audit and Tax Audit simultaneously. |
FAQ 22-04-2020 |
|
Whether the Auditor of a Bank can hold Credit card of the same Bank |
There is no prohibition in holding credit card of bank where a CA Firm 3 is Auditor of the Bank. Indebtedness will apply if there is outstanding balance of ₹ 10, 000/-* beyond prescribed credit period limit on credit card given to holder of credit card. * As per the limit of indebtedness existing as on date |
FAQ 22-04-2020 |
|
Whether the Concurrent Auditor of a Bank can accept the assignment of its Statutory Audit, after relinquishing the assignment of the Concurrent Audit of the Bank? |
Yes, the Concurrent Auditor of a Bank can choose to relinquish the Concurrent Audit, and accept the assignment of Statutory Audit. He can, of course, also choose to continue with the Concurrent Audit assignment, without accepting the Statutory Audit. Provided, where the Concurrent Audit Assignment for the relevant year has already been commenced at the time of acceptance of Statutory Audit, the Statutory Audit for the said year should not be accepted. |
FAQ 22-04-2020 |
|
Can Internal Auditor undertake Goods and Service Tax (GST) Audit simultaneously |
internal auditor of an assesee, whether working with the organization or independently practising Chartered Accountant being an individual chartered accountant or a firm of chartered accountants, cannot be appointed as his Tax auditor (under the Income Tax Act, 1961). Upon consideration, the Council has decided that based on the conflict in roles as statutory and internal auditor simultaneously, the bar on internal auditor of an entity to accept tax audit (under Income Tax Act, 1961) will also be applicable to GST Audit (under the Central Goods and Service Act, 2017). Accordingly, it is clarified that an Internal Auditor of an entity cannot undertake GST Audit of the same entity. |
378th Meeting of Council held on 26th and 27th September, 2018, |
|
Whether a member in practice is permitted to have his name published in Telephone Directory |
Yes, a member in practice is permitted to have his name published in the telephone directory subject to certain conditions |
Para (c) under Clause (6) of Part I of the First Schedule to the Act |
|
Can a Chartered Accountant provide ₹Portfolio Management Services’ (PMS) as part of CA practice? |
No, the Explanation to expressly bars the activities of broking, underwriting and Portfolio Management. |
Clause (xix) of the definition of ‘Management Consultancy and other Services’ as appearing in Appendix-3 |
|
Can a Chartered Accountant in practice seek professional work from his professional colleagues? |
a member is permitted to apply or request for or to invite or to secure professional work from another Chartered Accountant in practice. The issue of advertisement or a circular by a Chartered Accountant, seeking work from professional colleagues on any basis whatsoever is in violation of Clause (6) of Part I of the First Schedule to the Act. However, classified advertisement in the Journal/Newsletter of the Institute is permissible in this regard. A member is permitted to issue a classified advertisement in the Journal/Newsletter of the Institute intended to give information for sharing professional work on assignment basis or for seeking professional work on partnership basis or salaried employment in the field of accounting profession provided it only contains the accountant’s name, address, telephone, fax number and E-mail address. |
proviso (i) of Clause (6) of Part-I of the First Schedule |
|
Whether a member in practice can be a Director Simplicitor of a company? |
Yes, a member in practice is permitted generally to be a Director Simplicitor in a company provided he is not a Managing Director or Wholetime Director and is required only in the Board Meetings of the company and not paid any remuneration except for attending such meetings. Specific permission of the council is not required in this regard. |
FAQ July 2018 |
|
Can a member in practice print QR (Quick response) code on his visiting cards, facilitating easy access to information? |
Yes, printing of QR Code on the visiting Cards is permissible , provided that it does not contain information that is not otherwise permissible to be printed on a visiting Card. |
FAQ July 2018 |
7. Code of Ethics, 2019 (New) – to be effective from 01 July 2020
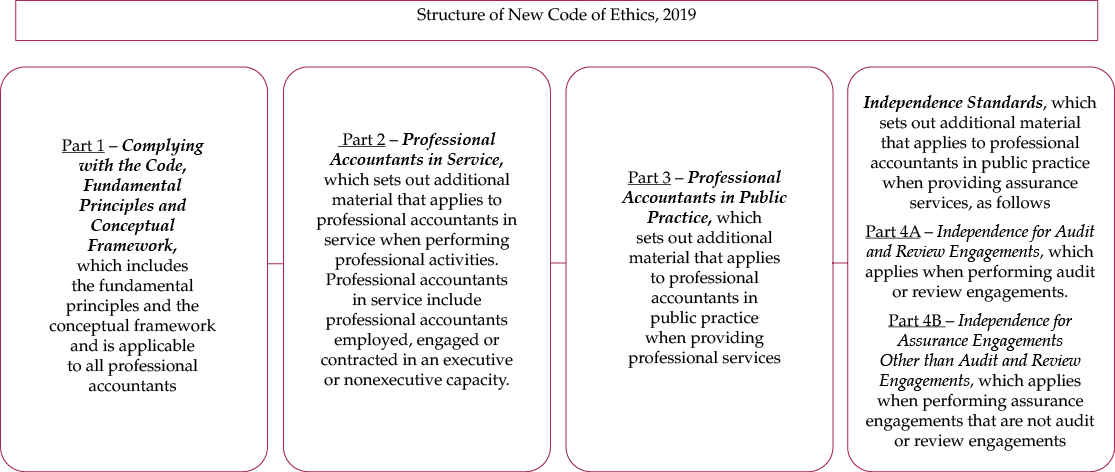
[Ref ICAI Publication on Code of Ethics – January 2019 Edition – Soft Copy available on Ethical Standard’s Board Page of ICAI - https://www.icai.org/new_post.html?post_id=958&c_id=50]
 |
The Code contains sections which address specific topics. Some sections contain subsections dealing with specific aspects of those topics. Each section of the Code is structured, where appropriate, as follows:
- Introduction– sets out the subject matter addressed within the section, and introduces the requirements and application material in the context of the conceptual framework. Introductory material contains information, including an explanation of terms used, which is important to the understanding and application of each Part and its sections.
- Complying with the Code requires knowing, understanding and applying:
- All of the relevant provisions of a particular section in the context of Part 1, together with the additional material set out in Sections 200, 300, 400 and 900, as applicable.
- All of the relevant provisions of a particular section, for example, applying the provisions that are set out under the subheadings titled “General” and “All Audit Clients” together with additional specific provisions, including those set out under the subheadings titled “Audit Clients that are not Public Interest Entities” or “Audit Clients that are Public Interest Entities.”
- All of the relevant provisions set out in a particular section together with any additional provisions set out in any relevant subsection.
- Requirements and application material are to be read and applied with the objective of complying with the fundamental principles, applying the conceptual framework and, when performing audit, review and other assurance engagements, being independent
- Complying with the Code requires knowing, understanding and applying:
- Requirements– establish general and specific obligations with respect to the subject matter addressed.
- Requirements are designated with the letter “R” and, in most cases, include the word “shall.” The word “shall” in the Code imposes an obligation on a professional accountant or firm to comply with the specific provision in which “shall” has been used.
- In some situations, the Code provides a specific exception to a requirement. In such a situation, the provision is designated with the letter “R” but uses “may” or conditional wording.
- When the word “may” is used in the Code, it denotes permission to take a particular action in certain circumstances, including as an exception to a requirement. It is not used to denote possibility.
- When the word “might” is used in the Code, it denotes the possibility of a matter arising, an event occurring or a course of action being taken. The term does not ascribe any particular level of possibility or likelihood when used in conjunction with a threat, as the evaluation of the level of a threat depends on the facts and circumstances of any particular matter, event or course of action.
- Application material– provides context, explanations, suggestions for actions or matters to consider, illustrations and other guidance to assist in complying with the requirements.
- In addition to requirements, the Code contains application material that provides context relevant to a proper understanding of the Code. In particular, the application material is intended to help a professional accountant to understand how to apply the conceptual framework to a particular set of circumstances and to understand and comply with a specific requirement. While such application material does not of itself impose a requirement, consideration of the material is necessary to the proper application of the requirements of the Code, including application of the conceptual framework. Application material is designated with the letter “A.”
- Where application material includes lists of examples, these lists are not intended to be exhaustive
- Appendix to Guide to the Codeprovides an overview of the Code.
- Part 1 – Complying with the Code (sec 100), Fundamental Principles (sec 110) and Conceptual Framework (sec 120)
Sec 120 - The conceptual framework specifies an approach for a professional accountant to:
- Identify threats to compliance with the fundamental principles;
- Evaluate the threats identified; and
- Address the threats by eliminating or reducing them to an acceptable level.
- Sub Sec 111 - Integrity
- Sub Sec 112 - Objectivity
- Sub Sec 113 - Professional Competence and Due Care
- Sub Sec 114 - Confidentiality
- Sub Sec 115 - Professional Behaviour
Breaches of the Code
R100.4 Paragraphs R400.80 to R400.89 and R900.50 to R900.55 address a breach of Independence Standards. A professional accountant who identifies a breach of any other provision of the Code shall evaluate the significance of the breach and its impact on the accountant’s ability to comply with the fundamental principles. The accountant shall also:
- Take whatever actions might be available, as soon as possible, to address the consequences of the breach satisfactorily; and
- Determine whether to report the breach to the relevant parties.
100.4 A1 Relevant parties to whom such a breach might be reported include those who might have been affected by it.
- Part 2 – Professional Accountants in Service
- Section 200 Applying the Conceptual Framework – Professional Accountants in Service
- Section 210 Conflicts of Interest
- Section 220 Preparation and Presentation of Information
- Section 230 Acting with Sufficient Expertise
- Section 240 Financial Interests, Compensation and Incentives linked to Financial Reporting and Decision Making
- Section 250 Inducements, Including Gifts and Hospitality
- Section 260 Responding to Non-Compliance with Laws and Regulations in case of employment with Listed Entities
- Section 270 Pressure to Breach the Fundamental Principles
- Part 3 – Professional Accountants in Public Practice
- Section 300 - Applying the Conceptual Framework – Professional Accountants in Public Practice
- Section 310 - Conflicts of Interest
- Section 320 - Professional Appointments
- Section 321 - Second Opinions
- Section 330 - Fees and Other Types of Remuneration
- Section 340 - Inducements, Including Gifts and Hospitality
- Section 350 - Custody of Client Assets
- Section 360 - Responding to Non-Compliance with Laws and Regulations during the course of Audit Engagements of Listed Entities
- Part 4A – Independence for Audit and Review Engagements
- Section 400 Applying the Conceptual Framework to Independence for Audit and Review Engagements
- Section 410 Fees
- Section 411 Compensation and Evaluation Policies
- Section 420 Gifts and Hospitality
- Section 430 Actual or Threatened Litigation
- Section 510 Financial Interests
- Section 511 Loans and Guarantees
- Section 520 Business Relationships
- Section 521 Family and Personal Relationships
- Section 522 Recent Service with an Audit Client
- Section 523 Serving as a Director or Officer of an Audit Client
- Section 524 Employment with an Audit Client
- Section 525 Temporary Personnel Assignments
- Section 540 Long Association of Personnel (Including Partner Rotation) with an Audit Client
- Section 550 Auditor Rotation
- Section 600 Provision of Non-Assurance Services to an Audit
- Subsection 601 – Accounting and Bookkeeping Services
- Subsection 602 – Administrative Services
- Subsection 603 – Valuation Services
- Subsection 604 – Tax Services
- Subsection 605 – Internal Audit Services
- Subsection 606 – Information Technology Systems Services
- Subsection 607 – Litigation Support Services
- Subsection 608 – Legal Services
- Subsection 609 – Recruiting Services
- Subsection 610 – Corporate Finance Services
- Section 800 Reports on Special Purpose Financial Statements that Include a Restriction on Use and Distribution (Audit and Review Engagements)
- Part 4B – Independence for Assurance Engagements Other than Audit and Review Engagements
- Section 900 - Applying the Conceptual Framework to Independence for Assurance Engagements Other than Audit and Review Engagements
- Section 905 - Fees
- Section 906 - Gifts and Hospitality
- Section 907 - Actual or Threatened Litigation
- Section 910 - Financial Interests
- Section 911 - Loans and Guarantees
- Section 920 - Business Relationships
- Section 921 - Family and Personal Relationships
- Section 922 - Recent Service with an Assurance Client
- Section 923 - Serving as a Director or Officer of an Assurance Client
- Section 924 - Employment with an Assurance Client
- Section 940 - Long Association of Personnel with an Assurance Client
- Section 950 - Provision of Non-Assurance Services to Assurance Clients Other than Audit and Review Engagement Clients
- Section 990 - Reports that Include a Restriction on Use and Distribution (Assurance Engagements Other than Audit and Review Engagements)
- Part 1 – Complying with the Code (sec 100), Fundamental Principles (sec 110) and Conceptual Framework (sec 120)
8. Continuing Professional Education – CPE hours requirement for the block period of 3 years (1st January, 2020 – 31st December, 2022)
- All the members (aged less than 60 years) who are holding Certificate of Practice (except all those members who are residing abroad) are required to:
- Complete at least 120 CPE credit hours in a rolling period of three years.
- Complete minimum 20 CPEcredit hours of structured learning in each calendar year.
- Balance 60 CPE credit hours (minimum 20 CPE credit hours in each calendar year) can be completed either through Structured or Unstructured learning (as per Member’s choice)
- All the members (aged less than 60 years) who are not holding Certificate of Practice and all the members who are residing abroad (whether holding Certificate of Practice or not) are required to:
- Complete at least 60 CPE credit hours either structured or unstructured learning (as per Member’s choice) in rolling period of three years.
- Complete minimum 15 CPEcredit hours of either structured or unstructured learning (as per member’s choice) in each calendar year.
- All the members (aged 60 years & above) who are holding Certificate of Practice, are required to:
- Complete at least an aggregate of 90 CPE credit hours of either structured or unstructured learning (as per member’s choice) in a rolling period of three years.
- Complete minimum of 20 CPE credit hours being an aggregate of either structured or unstructured learning (as per member’s choice) in each calendar year.
- The following class of members are exempted from CPE credit hours requirement:
- All the members (aged 60 years and above) who are not holding Certificate of Practice.
- Judges of Supreme Court, High Court, District Courts and Tribunals
- Members of Parliament/MLAs/MLCs
- Governors of States
- Centre and State Civil Services
- Entrepreneurs (owners of business (manufacturing) organisations other than professional services)
- Judicial officers
- Members in Military Service
- Temporary Exemptions:
- Female members for one Calendar year on the grounds of pregnancy
- Physically disabled members on case to case basis having permanent disability of not less than 40% and above (Supported with medical certificates from any doctor registered with Indian Medical Council with relevant specialisation as evidenced by Post Qualifications (M.D., M.S. etc.).
- Members suffering from prolonged critical diseases/illnesses or other disability as may be specified or approved by the CPEC. (Supported with medical certificates from any doctor registered with Indian Medical Council with relevant specialisation as evidenced by Post Qualifications (M.D., M.S. etc.)
- CPE Portal
The CPE Portal (http://www.cpeicai.org) has been developed to facilitate the members in keeping themselves updated with their CPE credit hours.
The members can view the status of CPE hours by logging into the CPE Portal using their User ID and password and verify their CPE attendance. Application of Unstructred CPE Hours should be submitted through the portal only. The portal also provides the information on upcoming events across India and abroad organised by various POUs such as Central Committees, Regional Councils, Foreign Chapters, CPE Chapters, CPE Study Circles and CPE Study Groups.
9. Peer Review
INTRODUCTION AND DEFINITIONS
Peer Review means an examination and review of the systems and procedures to determine whether they have been put in place by the Practice Unit for ensuring the quality of assurance services as envisaged by the Technical, Professional and Ethical Standards and whether the same were consistently applied in the period under review.
Practice Unit means members in practice, whether practising individually or a firm of Chartered Accountants.
Assurance Services means assurance engagement services as specified in the “Framework for Assurance Engagements” issued by the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India. There are certain specific exclusions like Management Consultancy Engagements, Representing a client before the authorities, etc.
Technical, Professional and Ethical Standards mean and include:
- Accounting, Standards issued by the ICAI and/or prescribed and notified by the Central Government of India;
- Standards issued by the ICAI;
Engagement Standards;
Statements;
Guidance Notes;
Standards on Internal Audit;
Statements on Quality Control;
- Notifications/Directions/Announcements/Guidelines/Pronouncements/Professional Standards issued from time to time by the Council or any of its committees.
- Framework for the preparation and presentation of financial statements, framework of statements and Standard on Auditing, Standard on Assurance Engagements, Standards on Quality Control and Guidance Notes on related services issued, from time to time,
by the ICAI and framework for assurance engagements. and - Various relevant Statutes and/or Regulations which are applicable.
SCOPE OF PEER REVIEW
The Peer Review process shall apply to all the assurance services of a practice unit. On selection of a practice unit for peer review, its assurance engagement records pertaining to the Peer Review period shall be subjected to review.
The focus during the review exercise will be on:
- Compliance with Technical, Professional and Ethical Standards;
- Quality of Reporting;
- Systems and procedures for carrying out assurance services;
- Training Programmes for staff concerned (including articled and audit assistants) with assurance functions, including appropriate infrastructure;
- Compliance with directions/guidelines issued by the ICAI including fees to be charged, number of audits undertaken and maintenance of assurance related records; and
- Compliance with directions/guidelines issued by the ICAI relating to article/audit assistants, including attendance register, work diaries, stipend payments and such other related records.
MEMBERS/FIRMS (PRACTICE UNIT) SUBJECT TO REVIEW
Every Practice Unit based on the category in which they fall are to be subjected to Peer Review. The Practice Units are categorised into Level I, II and III.
Any Practice Unit not selected for Peer Review may suo moto apply to the Board for the conduct of its Peer Review.
OBLIGATIONS OF THE PRACTICE UNIT
Any Practice Unit, in addition to the prescribed information to be furnished including the questionnaire, statements and such other particulars as the Board may deem fit shall provide access to any record or document required by the reviewer, which the reviewer reasonably believes to be of relevance to the peer review conducted.
PERIODICITY OF PEER REVIEW
The periodicity of Peer Review will be:
- Once in 3 years for Level I Practice Units;
- Once in 4 years for Level II Practice Units; and
- Once in 5 years for Level III Practice Units.
REPORT OF THE REVIEWER
- Preliminary Report
The reviewer before making his report to the Peer Review Board, communicate a preliminary report to the practice unit. The reviewer shall report the areas where systems and procedures were deficient or where non-compliance with reference to any other matter has been noticed by him. The practice unit shall make its submissions or written representations, in writing to the reviewer within 15 days of it receiving the preliminary report.
- Interim Report
The reviewer on receiving satisfactory reply from the practice unit shall submit an appropriate report to the Board. In case the reviewer is not satisfied with the reply of the practice unit, the reviewer shall accordingly submit a Modified Report to the Board, incorporating his reasons for the same.
On receiving a report from a reviewer, the Board, having regard to the Report and any submissions or representations attached to it, may make recommendations to the practice unit concerned regarding the application of Technical, Professional and Ethical Standards, regarding further improvements that could be made to internal quality systems.
A further “follow on” review after a period of 1 year from the date of issue of a modified report shall be ordered by the Board. The areas for improvement recommended with specific instructions will be carried out and implementation of the recommendations will be examined during the follow on review.
- Final Report
The reviewer will prepare a final report to the Board (The Reviewer’s Report), incorporating the findings as discussed with the practice unit.
The Board shall consider the report within a period of three months and if satisfied, will issue Peer Review Certificate. If not satisfied, it may issue recommendations to practice unit and direct the practice unit for follow on review after the period of 12 months to be conducted by a fresh reviewer appointed by the Board.
For Peer Reviews initiated on or ordered after April 1, 2014, if the Board is of the opinion that there are material deficiencies reported, then the Board shall refer the matter to the council for considering whether the same may be referred to the Disciplinary Directorate for initiating disciplinary action (Clause 8.5 of Peer Review Manual).
10. UDIN
Unique Documents Identification Number (UDIN), a unique number will be required to be generated for each and every document type being certified or attested by Practicing Chartered Accountants. Registration will be required to be done for the same at UDIN portal.
UDIN is mandatory from 1 st July 2019 for all Audit, Assurance and Attestation and Certification functions.
UDIN will ensure authenticity of documents, will enable the Government and other parties in obtaining certified documents, will promote accountability and transparency and help eliminate malpractices like forgery.
For further information and FAQs, refer https://udin.icai.org
ICAI announced on 19/04/2020 that 10 Year Membership/COP fees can be paid in advance, if paid so in lump sum there would be protection from escalation of fees if any.